1. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Generated by nearby electrical devices, power lines, or radio frequency (RF) transmissions.
2. Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): Caused by nearby radio transmitters, wireless devices, or microwave ovens.
3. Crosstalk: Occurs when signals from adjacent coaxial cables interfere with each other due to insufficient shielding or close proximity.
4. Impedance Mismatch: When there's a mismatch between the impedance of the coaxial cable and the connected devices, leading to signal reflections and degradation.
5. Grounding Issues: Poor grounding can introduce noise into the coaxial cable system, especially in areas with high electrical activity.
To mitigate these sources of interference, several measures can be taken:
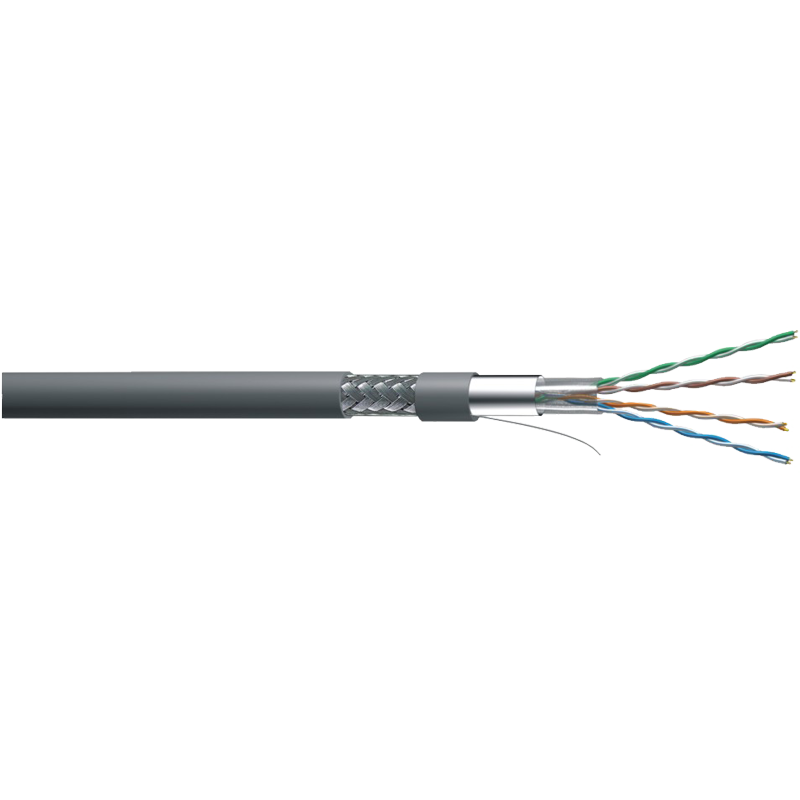
Use high-quality coaxial cable with adequate shielding: High-quality coaxial cables boast superior construction designed to minimize signal loss and maximize transmission efficiency. They typically feature multiple layers of shielding, such as aluminum foil, braided copper, or a combination of both, providing robust protection against external interference. These shielding layers act as barriers, preventing electromagnetic and radio frequency interference from penetrating the cable and disrupting signal integrity.
Properly terminate and ground the coaxial cable: Proper termination and grounding are fundamental aspects of coaxial cable installation that cannot be overstated. Termination involves the careful attachment of connectors, such as BNC or F-type connectors, to the coaxial cable's ends. It requires precise technique to maintain impedance matching and minimize signal loss at connection points. Improper termination can result in signal reflections, impedance mismatches, and degraded performance. Grounding, on the other hand, is essential for safety and signal integrity. By connecting the outer shielding of the coaxial cable to a reliable ground point, stray currents and static charges are safely dissipated, reducing the risk of electrical hazards and minimizing signal interference.
Employ ferrite beads or chokes on the cable: Ferrite beads or chokes are indispensable tools for combating high-frequency interference in coaxial cable systems. These passive electronic components are composed of a ferrite core encased in a conductive material and can be easily installed around the coaxial cable. Ferrite beads work by absorbing or attenuating unwanted electromagnetic noise, particularly in the radio frequency range, without significantly affecting the desired signal. They act as impedance filters, selectively blocking noise while allowing the desired signal to pass through unimpeded. Ferrite beads are available in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different cable diameters and frequencies, making them a versatile solution for mitigating interference in diverse applications.
Install surge protectors or filters: Surge protectors and filters play a crucial role in safeguarding coaxial cable systems against voltage spikes, power surges, and unwanted frequencies. Surge protectors are designed to divert excess voltage away from sensitive equipment, preventing damage and downtime caused by electrical transients. They typically feature fast-acting components, such as metal oxide varistors (MOVs) or gas discharge tubes (GDTs), which shunt overvoltage conditions to ground. Filters, on the other hand, are passive devices that selectively attenuate specific frequencies or harmonics to improve signal quality and reduce interference from nearby sources. They can be deployed at strategic points in the coaxial cable network to provide targeted protection against disruptive frequencies while allowing desired signals to pass through unaffected.
CAT5e S/FTP LAN Cable